Contents
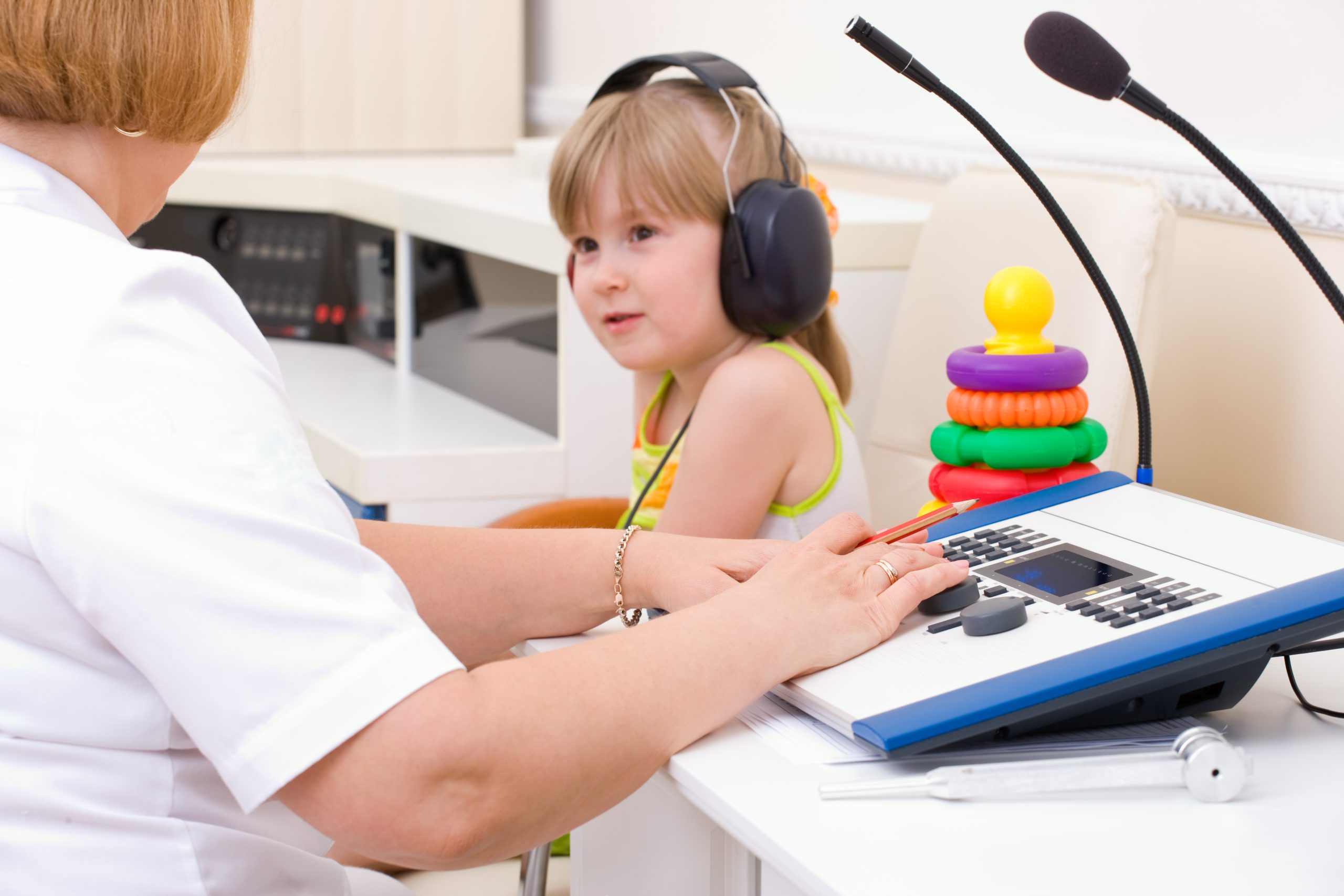
 According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, one in five Americans will be impacted by some form of hearing loss. With a growing demand for healthcare in this area, specialized practitioners are needed. An audiologist is a specialized healthcare professional who assesses, identifies, and manages hearing disorders. They work with a wide age range of patients, from newborns to the elderly. The career is in demand, but to establish yourself as an audiologist, you must have the proper audiologist schooling and training.
According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, one in five Americans will be impacted by some form of hearing loss. With a growing demand for healthcare in this area, specialized practitioners are needed. An audiologist is a specialized healthcare professional who assesses, identifies, and manages hearing disorders. They work with a wide age range of patients, from newborns to the elderly. The career is in demand, but to establish yourself as an audiologist, you must have the proper audiologist schooling and training.
How Do I Become an Audiologist?
Once you’ve made the decision on becoming an audiologist, you’ll learn to diagnose and treat patients suffering from:- peripheral hearing issues
- balance disorders
- other auditory problems
What Degree Do You Need to Be an Audiologist?
Bachelors’ Degree According to the Student Academy of Audiology (SAA), doctoral programs in audiology have widened their scope of approved academic disciplines. This means you don’t have to be an audiology major to get into an AudD program. Broad areas of science are accepted by most doctoral degree programs. Some of the most common majors include:- Biology
- Chemistry
- Engineering
- Physics
- Psychology
- Amplification
- Biological Foundations of Speech and Music
- Clinical Practice
- Psycho-acoustics
- Signals, Systems, and Acoustics for the Communication Sciences
- coursework
- clinical orientation
- observations
- practical assessments
- written qualifying exams
- Educational audiology
- geriatric audiology
- pediatric audiology

How Long Does It Take to Become an Audiologist?
Doctoral degrees in audiology (AudD) typically take four years to complete. However, you’ll need an bachelor’s degree to qualify for admission to enter a doctoral program. Bachelor’s degrees, in any discipline, traditionally take four years to complete. So, you’ll need to plan on spending eight years in school to become an audiologist if you go the traditional route. You may be able to speed up your journey by earning an accelerated bachelor’s degree. Some online programs offer accelerated pathways that allow you to earn your bachelor’s degree in less time. Two- and three-year bachelor’s programs are offered from accredited colleges and universities. This can allow students to cut time spent in school.Licenses and Certifications for Becoming an Audiologist
Once you’ve completed audiologist school, you’ll need licensing to practice. All states require audiologists to be licensed. Since most requirements vary by state, it’s important to contact your state’s licensing board to determine what’s needed. In addition to licensing, audiologists can earn a certification that helps improve job prospects and showcases certain skills. Offered by the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, the Certificate of Clinical Competence in Audiology (CCC-A), is one such certification. Audiologists may also become credentialed through the American Board of Audiology. Certifications are earned by graduating from an accredited doctorate in audiology program and passing a required standardized examination. There are several benefits to earning a certification. Audiologists prove their worth to employers, show a deeper knowledge of skills, and land better job prospects. In some states, employers may require certification. Other states allow certification in lieu of some education or training requirements needed to gain licensure.Other Important Qualities for Audiologists to Have
Now that you’ve determined which are the best degrees for audiologists, it’s important to assess if you’re a good fit for the career. Audiologists work with a specialized group of patients. In doing so, they must possess certain qualities specific to the needs of the population they care for. A career in audiology might suit you if you:- are a patient person by nature
- enjoy solving problems and facing challenges
- have a compassionate heart
 Below are several qualities and skills important to the career of an audiologist.
Below are several qualities and skills important to the career of an audiologist.
- Compassionate and caring: It’s not uncommon for an audiologist’s patients to arrive frustrated or under emotional distress due to the challenges faced. Patients may exhibit balance problems or have recently experienced hearing loss. Audiologists should meet their patients where they are at with compassion. They should be supportive and empathetic to their patients and equally supportive of their patient’s family members and caregivers.
- Critical thinking skills: When patients do not respond to treatments, audiologists rely on critical thinking skills to solve problems and come up with new and innovative treatment plans. In order to offer the best treatment, audiologists analyze data collected when testing a patient’s hearing. To determine a solid treatment plan, concentration and the ability to think critically are needed.
- Effective communication skills: Communication skills are important in any healthcare profession, particularly those that require face-to-face interaction and meeting with patients. Audiologists must communicate proposed care and treatments, diagnoses, and test results so that patients understand what is going on. They must be able to deliver complicated medical findings in a way that their patients understand. Audiologists also work closely with other healthcare professionals. They are part of an intricate medical team and must be able to communicate effectively to better care for their patients.
- Patience: Audiologists work with patients who require special attention and a lot of care. Their day-to-day interactions with patients require time and attention. As a result, audiologists must exhibit patience, tenderness, and understanding to help motivate and care for their patients.
- Problem-solving skills: Audiologists spend their day assessing and helping patients. During assessments, they determine the problems with hearing and balance. Through their problem-solving skills, they rule out causes until they pinpoint the origin of the issue. From there, audiologists figure out appropriate treatments to address the issues.
How Much Money Can an Audiologist Earn?
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for audiologists is $81,030. This number is nearly double that of the average salary for all occupations, which is reported by BLS as $41,950. Audiology is considered a top-paying field among healthcare professions. The top 10% of working audiologists see an even higher wage. BLS reports the highest 10% of earners in this occupation make more than $128,160. So, what can you do to improve your earnings potential as an audiologist? Various factors, such as years of experience, impact earnings. But the most significant fluctuation in earnings is a direct result of which industry you work in as an audiologist. According to BLS, there are four top-paying industries for audiologists. These include the following:- Hospitals (local, private, and state): $86,940
- Educational services: $83,500
- Occupational, physical, and speech therapy offices: $80,230
- Physician offices: $78,860
- states
- cities
- non-metropolitan areas
- North Dakota: $123,870 (annual mean wages)
- California: $115,540
- Maryland: $104,130
- Oklahoma: $101,810
- District of Columbia: $97,650
- Reno, Nevada: $151,460
- Tulsa, Oklahoma: $128,620
- Little Rock-North Little Rock-Conway, Arkansas: $127,210
- San Jose
- Santa Clara
- Los Angeles
- Long Beach
- Anaheim
- San Francisco
- Vallejo
- Myrtle Beach, South Carolina
- Greenville, North Carolina
- West Central North Dakota

What Is the Job Outlook for an Audiologist Career?
Once you have earned your audiology degree and decided to embark on the career path of an audiologist, it’s important to know what your job prospects will be. Luckily, the job outlook for this career is favorable. According to the BLS, audiologist jobs are in demand. In fact, we should see a 16% growth in employment of audiologists through 2030, which is twice the average employment growth for all occupations. Audiology is considered a small field, and an average of 800 openings are anticipated each year over the next decade. BLS reports that the openings should result from the need to replace audiologists who exit the labor force through retirement or transfer to different occupations. But even though audiology is a small occupation, the job growth will bring over 2,000 new jobs to the industry over the next 10 years. This growth is highly favorable for the occupation, as the employment growth for all healthcare diagnosing or treating practitioners is 12%. Audiology presents a much more favorable growth rate than many other occupations. So, what specifically will drive growth for this occupation? BLS suggests that an aging baby-boom population and increased life expectancies will impact the need for audiologists over the next several years. As the population ages, hearing loss and balance issues will become more prevalent. As a result, the aging population will drive the need for more audiologists. Also, due to technology advances, early identification of hearing disorders in infants should result in employment growth for audiologists. Technology advances for other populations will also drive employment growth. For example, sleep hearing aid design, smaller sizes, and the reduction of feedback make wearing these devices more comfortable than in years past. Due to the increased numbers of people seeking to minimize hearing loss, we should see a rise in employment for this occupation. In other words, now is an ideal time to seek out the best degree path for becoming an audiologist. For the next decade, the career remains in demand. Related Resources:- 30 Best Online Bachelor’s in Healthcare Administration
- 30 Great Small Colleges for STEM Degrees
- 30 Most Affordable Online Bachelor’s in Nursing Degrees from Private Colleges
- Ultimate Guide to Nursing & Healthcare Degrees and Careers
- Ultimate Guide to Science and Engineering Degrees and Careers
